CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT
Week 3
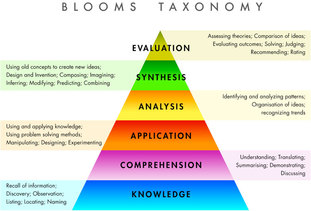
Philosophical foundations of curriculum :
Philosophy is defined as “ love of wisdom”. Philosophy is the beginning point in curriculum decision making and is the basis for all subsequent decisions regarding curriculum and it was the center of curriculum. Philosophy will help us on some question such as “what are schools for, what are subjects are of value and so on. The relationship of philosophy with school is to studies of learners, use of philosophy, studies contemporary life, suggestions from subject specialist and use of psychology of learning. Major of philosophy is like idealism, realism, pragmatism and existentialism.
Idealism is most to spiritual, moral or mental. Truth
and values are seen as absolute, timeless, and universal. For idealism, curriculum
is hierarchical. Concept and abstract subjects are the top subjects.
(Philosophy, theology).
Realism is where people can come to know the word through their senses and reason. Things will happen according to purpose and in orderly way. It is most focus on 3'R which is Reading, Writing and Arithmatic's. Besides, it has
organized separate subjects curriculum.
For example study of humankind experience becomes history subject.
Pragmatism is referred
to as experimentalism, based on change, process, and relativity. There are nothing
can be viewed intelligently except in relation to a pattern. For curriculum, it was views
teaching as more exploratory than explanatory.
Existentialism is stress
in individualism and personal self-
fulfillment. It prefers to free learner to choose what to study
and determine what is truth. It also consists of experiences
and subjects that lend themselves to philosophical dialogue
and acts of choice making: Literature, drama, film-making,
art, etc.Classroom would be rich in materials.
There also another major of philosophy such as
perennialism, essentialism, progessivism and
reconstructionism.
Historical foundation of curriculum
Why is it important to
know curriculum’s historical foundations? It is because a knowledge of curriculum’s history provides guidance for today’s
curriculum makers. We begin our discussion with the colonial period and proceed
through the 18th, 19th, and 20th centuries. Most of our discussion focuses on
the past 100 years. As we know, each country has its own history of education. Such
as American, their history of
education is from colonial, transitional and national period. For our country
it was
Malacca
sultanate, British, Japan, Pre-Independent- post independent.
Types of colonial schools is like Town
school, paranoid school, colleges, academies, Latin Grammar school and Privates
school. National period start from 1776
until 1850. At this time, we are with new government came a new mission for
schools, saw the first laws to mandate the existences of schools in certain
communities.